 Object
Object
Type
The object type: curve, surface, polysurface, block name, etc. displays.
Name
Object names are stored in the Rhino 3DM file and exported to file formats that accept object names.
See: Naming conventions in Rhino
Naming conventions in Rhino.
Layer
To change the object's layers, select a layer from the list. Layers can be created, and their properties can be changed in the Layer dialog box.
Display Color
The color of the object can either inherit the color of its layer or be set as an object property.
By Layer
Uses the display color of the object's layer.
By Parent
This option is only useful for objects in blocks. Think of a block instance as a container that contains objects (block members). A block instance is the parent of its block members. A block instance has its own properties. If By Parent is selected in the properties of a block member, the properties will be controlled by the block instance.
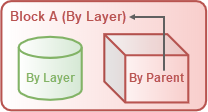
Simple block example:
-
In this example, Block A contains a cylinder and a box. The Display Color of the box is By Parent and is controlled by its parent (Block A). The box will display Block A's layer color because the display color of Block A is By Layer. The cylinder will always display its own layer color and will not be changed by Block A.
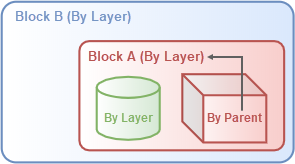
Nested block example:
-
Now Block A is nested in Block B. The box still displays Block A's layer color because By Parent only works with the direct parent.
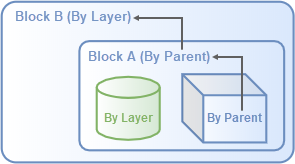
-
If the Display Color of Block A is changed to By Parent, the display color of the box will be indirectly controlled by its grandparent (Block B).
Specified color
Uses a specified color.
Linetype
By Layer
Uses the linetype of the object's layer.
By Parent
This option is only useful when creating blocks.
If an object's properties are By Parent, the object will continue to draw as if set to By Layer. However, when the object is part of a block, it takes on the properties of the block instance (layer or property).
Specified linetype
Uses a specified linetype:
Continuous

Border
Center
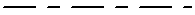
DashDot
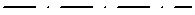
Dashed
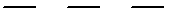
Dots
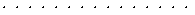
Hidden

Print Color
By Display
Prints using the display color.
By Layer
Prints using the layer color.
By Parent
Prints using the By Parent color.
Specified color
Prints using the specified color.
Print Width
By Layer
Prints using the layer print width.
Default
Prints using the default print width.
By Parent
Prints using the By Parent print width.
Custom width
Prints using a print width from the list. You can also type a number to customize the print width.
To define your own line widths, add line width values to the printwidths.txt file in the Rhino support folder.
In the printwidths.txt file:
- Lines begin with ; or // will be ignored.
- Line width values have to be larger than 0.
No Print
Does not print.
Custom Mesh
Turns custom mesh settings on and off.
Settings
Adjust...
Adjusts mesh settings to control the object mesh density. An object's custom mesh initializes with Document Mesh settings.
Rendering
Casts shadows
Casts shadows on other objects and a ground plane.
Receives shadows
Receives shadows from other objects.
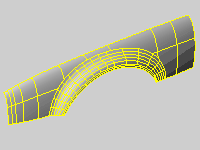
Density
Defines the number of isoparametric curves Rhino draws on the surface.
| Value | Display |
|---|---|
|
0 |
One isocurve at each knot; no isocurves on knot-free spans. |
|
1 |
One isocurve at each knot, or one isocurve on knot-free spans. |
|
2 |
One isocurve at each knot, plus one isocurve between knot locations. |
|
3 |
One isocurve at each knot, plus two isocurves between knot locations. |
Show surface isocurve
Turns display of surface isoparametric curves.
To change the default isoparametric curve density for new objects
- Go to Options > General.
Match
Set the properties of the selected object to match properties of another object in the model.
To match properties
- Select an object with the properties to match.
- Check the boxes for the properties to match.
Details
Displays technical information of the selected object.
See: What.
Object Description
The object type: curve, surface, polysurface, block name, etc. displays.
Object ID
The object's internal identification number.
Layer name
The name of the layer assigned to the object.
Render Material
The name of the render material assigned to the object.
Source
Object, layer, or parent.
Index
The layer material index number.
Geometry
Details about the geometry mathematics, edges, vertices, and meshes.